

Let's create a grouped bar graph maker for this record. Their responses are recorded in the following table: Name of favorite Sport
#Two bar histogram maker how to
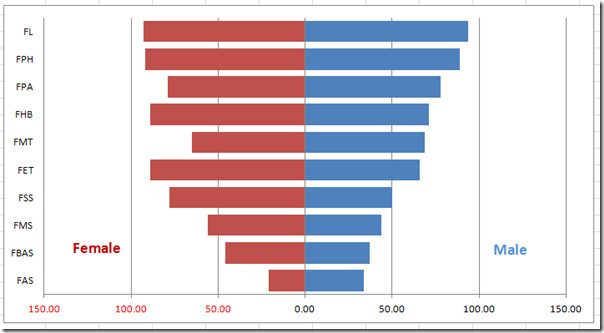
Try making a bar graph for the monthly expenses of your family for the past 1 year.Īfter having learned how to make a bar graph, let's dive into creating a bar graph online.Ī survey was conducted for students of grade 6 on their favorite sport. Suitable scale - Calculate the range of data to decide that. Legend - It helps readers understand what the bars refer to, similar to the one used in the map.ĥ. These rectangular columns represent the numerical data of the items given on the x-axis.įollowing are the essential components of a bar graph:Ĥ. On the x-axis, draw columns (or bars) of equal width for the heights calculated in the above step. Therefore, 15 lbs are represented by a bar of height 3 units on the graph. Suppose you choose a scale: On the y-axis 1 unit = 5 lbs. On the vertical bar, determine the height of the bar for the numerical data to be plotted. Write the names of the data (independent variables) whose values are to be plotted below the horizontal axis.Ĭhoose a suitable scale for values on the y-axis, i.e the dependent variables. The horizontal line is called the x-axis and the vertical line is called the y-axis.Īlong the x-axis (horizontal), mark the points at equal intervals. Take a graph paper and draw a horizontal line OX and a vertical line OY. Have a glance at various other types of bar charts.īelow are the steps to create a bar graph (also called a bar chart) on a graph paper. What we saw in the above case was a grouped bar graph. When the bars are arranged next to one another, it becomes convenient for the observer to compare different bars, or values, at a glance.ĭepending on the situations, different types of bar graphs are used. "A bar graph is a representation of numerical data in pictorial form of rectangles (or bars) having uniform width and varying heights."īar graphs, also known as column graphs, use vertical or horizontal bars to represent data.
So, she converted it into the form of a bar graph.Ĭonverting that data into a bar graph, provided Sia with a different and more effective way of looking at the same information.Ī bar graph, also called a bar chart, can make it much easier to notice trends that are not as obvious when viewing the raw data or tabular data. Looking at the table, it was really difficult for her to notice trends and analyze the data. Par(mar=c(5,8,4,2)) # increase y-axis margin.īarplot(counts, main="Car Distribution", horiz=TRUE, names.arg=c("3 Gears", "4 Gears", "5 Gears"), cex.names=0.Sia is having a look at the record of the average monthly expenses of two families. Par(las=2) # make label text perpendicular to axis Additionally, you can use graphical parameters such as the following to help text spacing: Values smaller than one will shrink the size of the label. You can decrease the font size using the cex.names = option.
With many bars, bar labels may start to overlap. Include the option axis.lty=1 to draw it. Use the aggregate( ) function and pass the results to the barplot( ) function.īy default, the categorical axis line is suppressed. You can create bar plots that represent means, medians, standard deviations, etc. Xlab="Number of Gears", col=c("darkblue","red"),īar plots need not be based on counts or frequencies. # Stacked Bar Plot with Colors and Legendīarplot(counts, main="Car Distribution by Gears and VS", (To practice making a simple bar plot in R, try this interactive video.) Stacked Bar Plot # Simple Horizontal Bar Plot with Added Labelsīarplot(counts, main="Car Distribution", horiz=TRUE, The option horiz=TRUE to createa a horizontal barplot. Include option names.arg=( character vector ) to label the bars. If height is a matrix and beside=TRUE, then the values in each column are juxtaposed rather than stacked. If height is a matrix and the option beside=FALSE then each bar of the plot corresponds to a column of height, with the values in the column giving the heights of stacked “sub-bars”. If height is a vector, the values determine the heights of the bars in the plot. Create barplots with the barplot( height ) function, where height is a vector or matrix.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
